Chances are, earwax and its buildup haven’t been subjects of extensive contemplation for you, except perhaps during ear hygiene routines. Nonetheless, understanding what causes earwax, how it forms, and its purpose is essential.
What triggers the buildup of earwax?
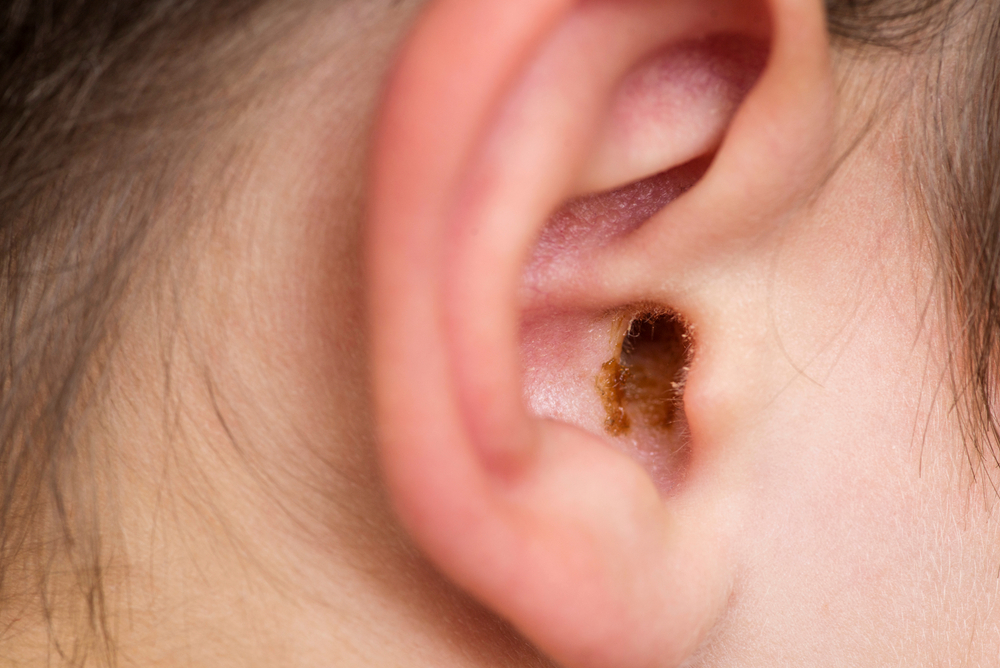
Earwax, scientifically known as cerumen, is a dense combination of debris, hair, skin particles, sweat, and ceruminous gland secretions nestled within the outer ear canal—the region between the middle and outer ear. This earwax presents with a waxy texture and can exhibit shades of orange, yellow, gray, or brown.
While the production levels of earwax differ from person to person, adults typically generate less earwax than children. Moreover, adult earwax tends to be darker and harder compared to that of children.
Earwax passes the outer ear canal leisurely, eventually reaching the ear opening, where it either self-expels or gets washed away during bathing.
Why is earwax essential?
Earwax serves several crucial functions, such as:
- Acting as a protective barricade against external irritants such as dirt, dust, and other foreign particles before they infiltrate deeper into the ear.
- Safeguarding and moisturizing the skin lining the ear canal, thereby preventing dryness and itchiness.
- Fending off potential infections that might arise within the ear canal.
Obstructions caused by earwax
Typically, there’s no imperative need to remove earwax from your ears unless it becomes impacted—a prevalent issue associated with earwax. Impacted earwax can stem from narrow or unusually shaped ear canals hindering the natural movement of earwax towards the ear’s periphery.
Improper ear hygiene practices, such as using Q-tips or bobby pins, can inadvertently push wax deeper into the ear canal.
Individuals grappling with hearing loss who use earplugs or hearing aids are also predisposed to experiencing ear canal blockages.
How excessive earwax can impact hearing
The presence of earwax blockages may yield mild discomfort and dampen auditory health.
Additionally, substantial accumulations of earwax can induce tinnitus—a sensation of ringing in the ears.
Neglected earwax blockages may escalate into middle ear infections, perforated eardrums, or enduring hearing impairment due to acoustic trauma.
Addressing impacted earwax
Should you suspect an earwax blockage, consulting your hearing specialist promptly is imperative. Depending on the severity of the obstruction, you may be advised to utilize over-the-counter wax softening drops or a bulb syringe for gentle irrigation to alleviate the condition.
Find a hearing specialist near you if you are concerned about your earwax buildup.